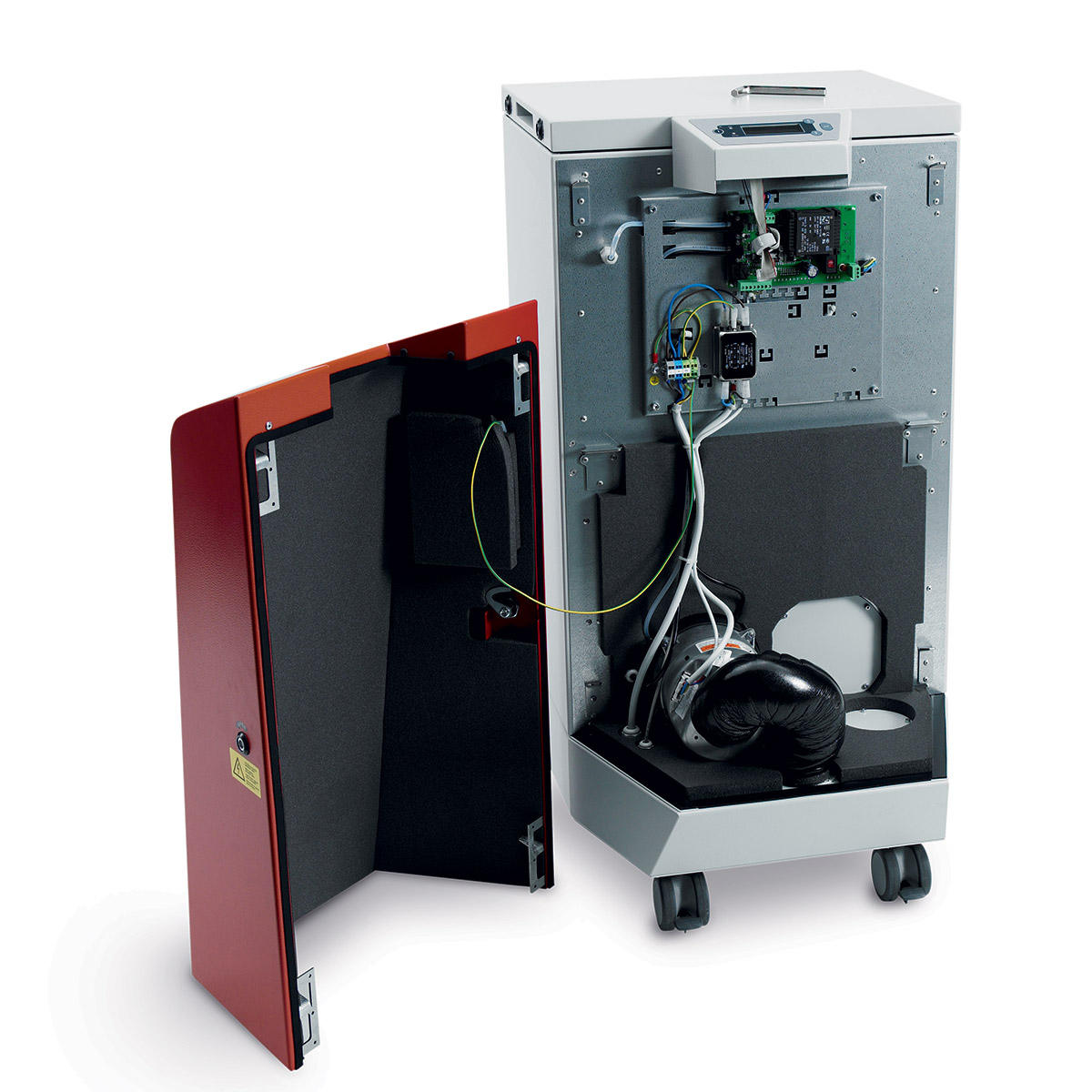
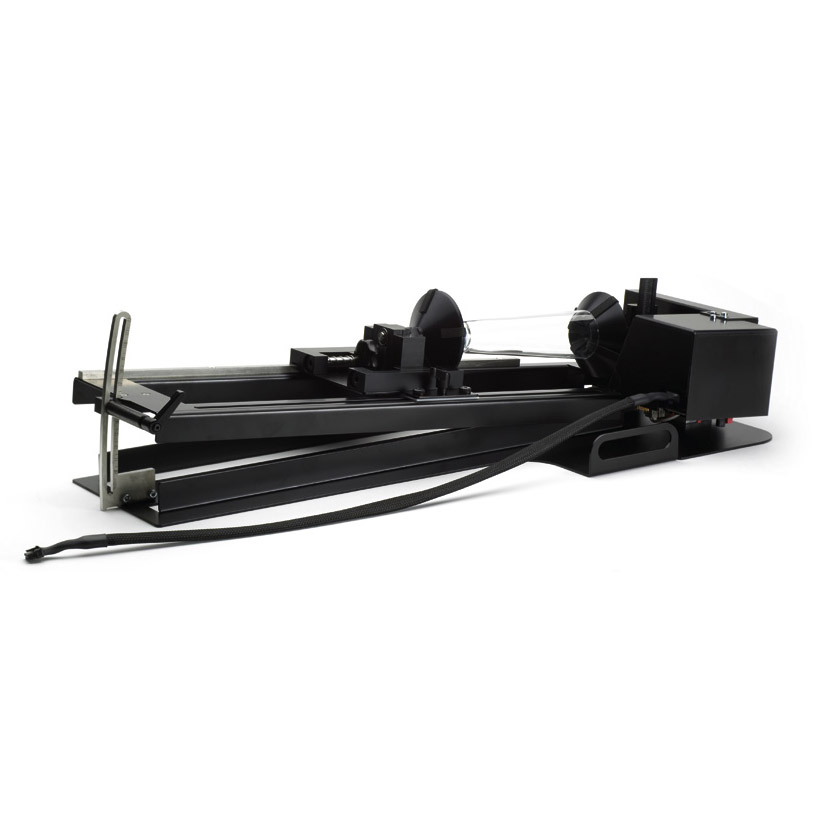
UV lasers, or ultraviolet lasers, produce light with a wavelength of 355 nm, which is much shorter than visible light or traditional fiber lasers (1064 nm). The light beam from the laser excitation diodes passes through three crystals in turn. The first has a wavelength of 1064 nm, the second has a wavelength of 532 nm (green laser), and the third has a wavelength of 355 nm (UV laser). Each crystal reduces the power, which is why UV lasers have a relatively low power of 3-10 W. Since the UV laser wavelength spectrum is highly absorbent, the marked area is only minimally thermally stressed (so-called cold marking). The diameter of the laser spot is proportional to the wavelength of the light it produces – i.e. very small. This makes UV lasers ideal for applications where achieving fine details or minimal material damage is crucial. They are also applicable for materials that generally cannot be marked with a fiber or green laser.
Main applications include:
-
Marking plastics, glass, ceramics and electronics:
Due to their shorter wavelength (typically 355 nm), they minimize thermal effects, which is key for marking sensitive materials.
-
Micromachining:
UV lasers are used for precise cutting, drilling and other micromachining of thin materials, for example in the semiconductor industry.
-
Semiconductor and PCB manufacturing:
UV lasers are ideal for micro-lithography and other processes associated with electronics manufacturing.
-
Marking medical instruments and implants:
UV lasers enable hygienic and precise marking without contaminating the material.
-
Material removal:
They are used for selective removal of layers of materials, for example in the production of displays or LEDs.
-
Marking on highly reflective materials:
In some cases, UV lasers are also suitable for materials that are difficult to process with other types of lasers.
Important features of UV lasers:
- High precision: UV lasers allow you to create very fine and precise patterns.
- Minimal thermal impact: Due to their short wavelength, UV lasers cause minimal thermal damage to the material.
- Versatility: UV lasers are suitable for a wide range of materials.
- High speed: Modern UV lasers offer high marking and processing speeds.
We offer three UV laser configuration options depending on the requirements. A JPT or IPG laser source can be used in combination with a VonJan or Raylase scanner head.